
Expertise
Improving intestinal health in livestock
By infuencing intestinal functionality, animals become more resilient. But what can we do to influence gut health? Research by Wageningen Livestock Research provides answers.
The animal's intestinal health can be influenced by different factors. One of these factors is the microbiome, a collection of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that an animal carries in, for example, its intestines. Other host factors include the immune system and the intestinal tissue. External factors include animal feed, genetics, and housing systems. In Wageningen, we study these factors in an interdisciplinary teams and together with partners.
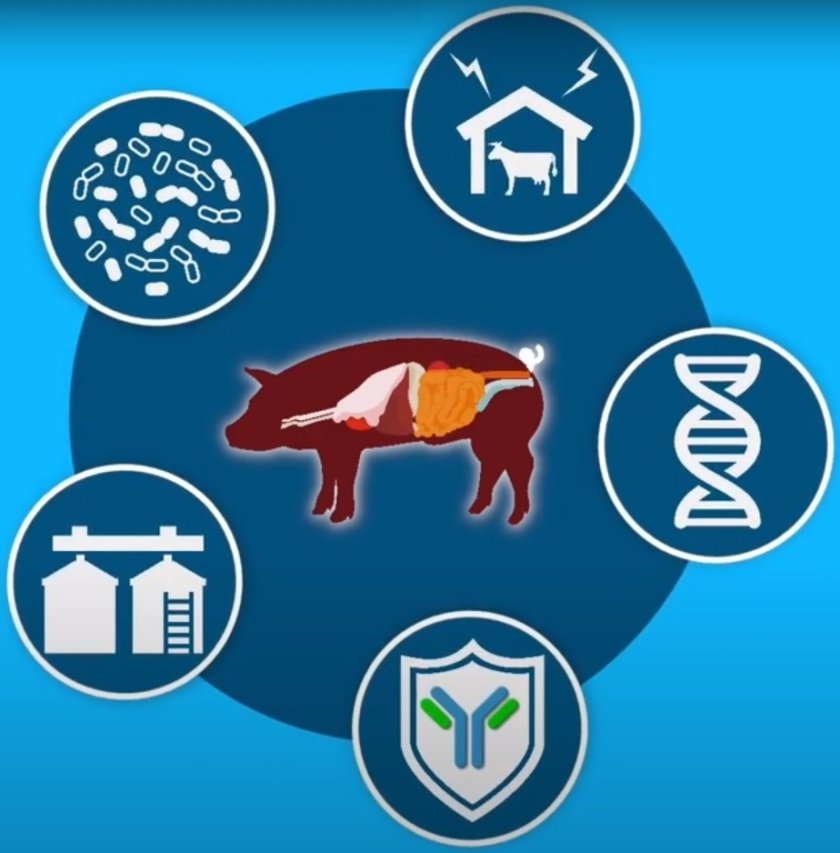
Factors of influence:
- Microbiota
- Immune system
- Animal feed
- Genetic potential
- Housing systems
Improved gut health in poultry, pigs and cattle
The gastro-intestinal tract of farm animals is the location where nutrient digestion and absorption takes place. Adequate availability of nutrients in a balanced ratio is a keystone for efficient and sustainable animal production. However, additional functions of the gut have been associated to its barrier function and the presence of an extensive microbiome. The microbiome plays a role in immune development in farm animals and in the capacity to respond to health and dietary challenges. Moreover, the intestinal microbiome and its metabolites communicate with other organs and tissues in the body affecting their responses and metabolism.
A proper functioning of the digestive tract with its very diverse functions and support of intestinal health is therefore key for productivity, health, and well-being of farm animals.
- Unfortunately, your cookie settings do not allow videos to be displayed. - check your settings
Can we prevent or reduce intestinal disorders?
Yes, we can. By adopting preventive approaches such as appropriate dietary strategies and combining that with smart managemental practices in animal husbandry. Such preventive approaches will allow to raise more resilient farm animals with optimal productive performance while safeguarding animal welfare.
How can we reduce antibiotic use in animals?
By employing a multifaceted approach, including animal nutrition, genetics, and behavior, it is possible to increase the resilience and robustness of animals. This reduces the animal’s disease susceptibility and incidence. Consequently, less antibiotics or other veterinary drugs will be used to treat animals with clinical infections and diseases.
Questions we can help provide answers to
What is the mode-of-action of feed additives in improving intestinal health and functionality?
Feed additives included in diets for farm animals often have multiple effects and are targeted to support their productivity, health, and well-being. In part, they relate to gut functionality and gut health. The gut has important digestive and barrier functions. The intestinal microbiome plays an important role in an optimal barrier function. To maximize the efficacy and value of feed additives the in vivo mode-of-action in target animal species needs to be known.
How can molecular biology and biotechnology help in understanding functional properties of feed ingredients?
The diet and its feed ingredients provide first of all nutrients to the animal supporting productivity and contributing to a sustainable animal production. However, ingredients in the diet can also induce other potential beneficial effects to animals ingesting them. They can relate to the presence of bioactive compounds or to specific effects on the intestinal microbiome or functioning of the gastro-intestinal system. To identify such effects in-depth studies are required focusing on effects on specific organs and tissues using advanced state-of-the-art ‘omics and bioinformatic tools. These 'omics and tools include e.g. transcriptomics (gene expression), proteomics, metabolomics, and metagenomics (microbiota composition and activity).
What are the benefits of using in vitro systems, such as mini-guts (intestinal organoids), in understanding intestinal functionality?
Organoids or mini-organs grown in Petri dishes and have enormous potential in basic, translational- and applied-research. For instance, organoids have great potential as an in vitro research tool on a number of fields of research in animal nutrition, animal breeding, host-microbe interactions, and animal biotechnology. Furthermore, organoids as in vitro models offer a great possibility to reduce the use of experimental animals.
Read more about the benefits and utility of intestinal organoids in understanding intestinal functionality.
What is the impact of early life interventions on intestinal functionality and health?
Early life interventions have shown to greatly impact the intestinal functionality, i.e. colonization of the intestinal microbiota and programming of the host immune system. Moreover, long-lasting effects have been shown on intestinal functionality after an early life intervention. This emphasizes the importance of giving animals the most optimal start in life.
What is the mechanism between microbiome, immune and behavior (brain-gut-immune interaction)?
There is ample evidence that animal welfare and behavior is significantly impacted by the gut-brain axis. Rodent studies have shown that the gut-microbiota influences behavioral characteristics, such as anxiety, stress and activity. In poultry and pigs, the concept of the gut-brain axis is still poorly investigated. We have recently demonstrated that the (gut) microbiota can influence welfare and behavior in poultry. Vice versa, there is also evidence that improved poultry welfare might impact microbiota diversity via bidirectional gut-brain communication. We have recently observed that on-farm hatching and application of a so-called ‘dark brooder’ can benefit poultry welfare and alter microbial gut colonization. In pigs, we have shown that susceptibility to viral (PRRSV) infection was reduced and the (gut) microbiota composition was altered in pigs kept in enriched housing/pens.
Can we improve efficacy of the vaccination program by supporting intestinal health or functionality?
Often conventional vaccination programmes are associated with low intake and reduced growth performances at critical phases in farm animal species, which may result in carry-over effects resulting to decreased survival and/or market/carcass weights. By providing appropriate feed-additives in the diet and right housing conditions at the critical phases in farm animal species one can alleviate the negative impact on productive performance associated with vaccinations.